CF195E Building Forest
Description
An oriented weighted forest is an acyclic weighted digraph in which from each vertex at most one edge goes.
The root of vertex $ v $ of an oriented weighted forest is a vertex from which no edge goes and which can be reached from vertex $ v $ moving along the edges of the weighted oriented forest. We denote the root of vertex $ v $ as $ root(v) $ .
The depth of vertex $ v $ is the sum of weights of paths passing from the vertex $ v $ to its root. Let's denote the depth of the vertex $ v $ as $ depth(v) $ .
Let's consider the process of constructing a weighted directed forest. Initially, the forest does not contain vertices. Vertices are added sequentially one by one. Overall, there are $ n $ performed operations of adding. The $ i $ -th $ (i>0) $ adding operation is described by a set of numbers $ (k,v_{1},x_{1},v_{2},x_{2},...\ ,v_{k},x_{k}) $ and means that we should add vertex number $ i $ and $ k $ edges to the graph: an edge from vertex $ root(v_{1}) $ to vertex $ i $ with weight $ depth(v_{1})+x_{1} $ , an edge from vertex $ root(v_{2}) $ to vertex $ i $ with weight $ depth(v_{2})+x_{2} $ and so on. If $ k=0 $ , then only vertex $ i $ is added to the graph, there are no added edges.
Your task is like this: given the operations of adding vertices, calculate the sum of the weights of all edges of the forest, resulting after the application of all defined operations, modulo $ 1000000007 $ $ (10^{9}+7) $ .
Input Format
N/A
Output Format
N/A
Explanation/Hint
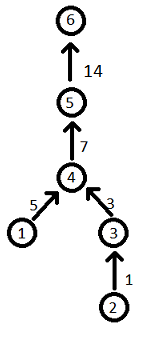
Conside the first sample:
1. Vertex $ 1 $ is added. $ k=0 $ , thus no edges are added.
2. Vertex $ 2 $ is added. $ k=0 $ , thus no edges are added.
3. Vertex $ 3 $ is added. $ k=1 $ . $ v_{1}=2 $ , $ x_{1}=1 $ . Edge from vertex $ root(2)=2 $ to vertex $ 3 $ with weight $ depth(2)+x_{1}=0+1=1 $ is added.
4. Vertex $ 4 $ is added. $ k=2 $ . $ v_{1}=1 $ , $ x_{1}=5 $ . Edge from vertex $ root(1)=1 $ to vertex $ 4 $ with weight $ depth(1)+x_{1}=0+5=5 $ is added. $ v_{2}=2 $ , $ x_{2}=2 $ . Edge from vertex $ root(2)=3 $ to vertex $ 4 $ with weight $ depth(2)+x_{1}=1+2=3 $ is added.
5. Vertex $ 5 $ is added. $ k=1 $ . $ v_{1}=1 $ , $ x_{1}=2 $ . Edge from vertex $ root(1)=4 $ to vertex $ 5 $ with weight $ depth(1)+x_{1}=5+2=7 $ is added.
6. Vertex $ 6 $ is added. $ k=1 $ . $ v_{1}=3 $ , $ x_{1}=4 $ . Edge from vertex $ root(3)=5 $ to vertex $ 6 $ with weight $ depth(3)+x_{1}=10+4=14 $ is added.
The resulting graph is shown on the pictore below: