CF402D Upgrading Array
Description
You have an array of positive integers $ a[1],a[2],...,a[n] $ and a set of bad prime numbers $ b_{1},b_{2},...,b_{m} $ . The prime numbers that do not occur in the set $ b $ are considered good. The beauty of array $ a $ is the sum 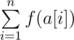, where function $ f(s) $ is determined as follows:
- $ f(1)=0 $ ;
- Let's assume that $ p $ is the minimum prime divisor of $ s $ . If $ p $ is a good prime, then 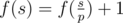, otherwise 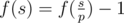.
You are allowed to perform an arbitrary (probably zero) number of operations to improve array $ a $ . The operation of improvement is the following sequence of actions:
- Choose some number $ r $ ( $ 1
Input Format
N/A
Output Format
N/A
Explanation/Hint
Note that the answer to the problem can be negative.
The GCD( $ x_{1} $ , $ x_{2} $ , ..., $ x_{k} $ ) is the maximum positive integer that divides each $ x_{i} $ .