CF444B DZY Loves FFT
Description
DZY loves Fast Fourier Transformation, and he enjoys using it.
Fast Fourier Transformation is an algorithm used to calculate convolution. Specifically, if $ a $ , $ b $ and $ c $ are sequences with length $ n $ , which are indexed from $ 0 $ to $ n-1 $ , and
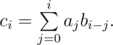We can calculate $ c $ fast using Fast Fourier Transformation.
DZY made a little change on this formula. Now
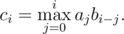To make things easier, $ a $ is a permutation of integers from $ 1 $ to $ n $ , and $ b $ is a sequence only containing $ 0 $ and $ 1 $ . Given $ a $ and $ b $ , DZY needs your help to calculate $ c $ .
Because he is naughty, DZY provides a special way to get $ a $ and $ b $ . What you need is only three integers $ n $ , $ d $ , $ x $ . After getting them, use the code below to generate $ a $ and $ b $ .
```
//x is 64-bit variable;
function getNextX() {
x = (x * 37 + 10007) % 1000000007;
return x;
}
function initAB() {
for(i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1){
a[i] = i + 1;
}
for(i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1){
swap(a[i], a[getNextX() % (i + 1)]);
}
for(i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1){
if (i < d)
b[i] = 1;
else
b[i] = 0;
}
for(i = 0; i < n; i = i + 1){
swap(b[i], b[getNextX() % (i + 1)]);
}
}
```
Operation x % y denotes remainder after division $ x $ by $ y $ . Function swap(x, y) swaps two values $ x $ and $ y $ .
Input Format
N/A
Output Format
N/A
Explanation/Hint
In the first sample, $ a $ is $ [1\ 3\ 2] $ , $ b $ is $ [1\ 0\ 0] $ , so $ c_{0}=max(1·1)=1 $ , $ c_{1}=max(1·0,3·1)=3 $ , $ c_{2}=max(1·0,3·0,2·1)=2 $ .
In the second sample, $ a $ is $ [2\ 1\ 4\ 5\ 3] $ , $ b $ is $ [1\ 1\ 1\ 0\ 1] $ .
In the third sample, $ a $ is $ [5\ 2\ 1\ 4\ 3] $ , $ b $ is $ [1\ 1\ 1\ 1\ 0] $ .